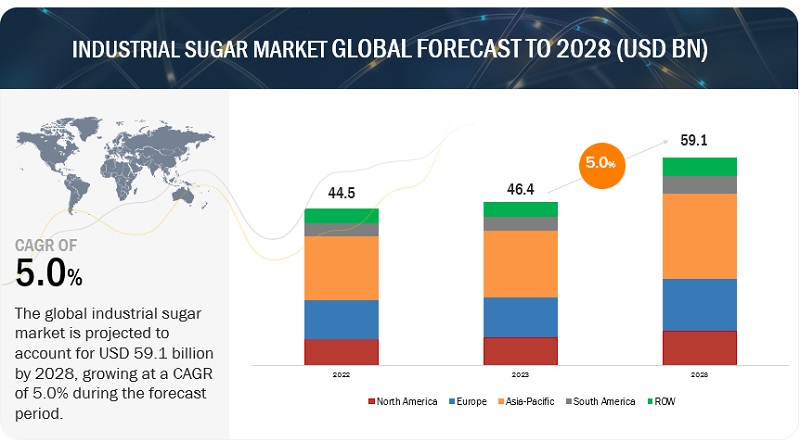
The global sugar market is navigating a complex landscape characterized by fluctuating prices and evolving dynamics in production and demand. Recent trends in the sugar markets have been significantly influenced by a variety of factors, including unpredictable weather patterns, production levels, and shifting trade policies. Understanding these elements is crucial for investors and stakeholders aiming to anticipate future movements in sugar prices and market behavior.
Current Market Overview
According to Trading Economics, sugar prices have exhibited volatility, reflecting the interplay of demand and supply forces coupled with geopolitical and environmental factors. The sugar market is sensitive to changes in production forecasts which are often influenced by weather conditions in key producing regions such as Brazil, India, and Thailand.
Production Dynamics
Brazil, the world's largest sugar producer, has seen its sugar output affected by adverse weather conditions, including droughts and frosts. These environmental challenges have disrupted the harvest and subsequently impacted global supply. Similarly, India, another major player in the sugar market, has had to contend with monsoon variability, which directly affects cane yield and sugar output.
Thailand, traditionally a significant exporter, has also faced production setbacks due to unfavorable weather conditions. These disruptions in the major producing countries have tightened global supply, contributing to upward pressure on sugar prices.
Price Movements
The volatility in sugar prices can be traced back to several underlying factors. The most immediate influence is the production forecast; any reduction in expected output tends to drive prices up due to anticipated shortages. Additionally, the global sugar market is highly responsive to changes in energy prices, particularly oil, as sugarcane is a primary feedstock for ethanol production. When oil prices rise, sugarcane is often diverted for ethanol production, reducing sugar supply and pushing prices higher.
Trade policies and tariffs also play a critical role. For instance, the imposition of tariffs by major importing countries can alter trade flows and affect global sugar availability and pricing. The recent geopolitical tensions and trade negotiations have added layers of complexity to this already volatile market.
Key Market Drivers
-
Weather Conditions: As highlighted earlier, weather unpredictability remains a primary driver of sugar market trends. The reliance on agriculture makes the sugar market particularly susceptible to climate variations.
-
Energy Prices: The correlation between sugarcane and ethanol production links the sugar market to energy prices. Rising oil prices can translate to higher sugar prices as more sugarcane is used for ethanol.
-
Trade Policies: Tariff changes and trade agreements can disrupt traditional trade routes and affect global sugar prices. Recent negotiations and policy shifts have had a noticeable impact.
-
Currency Fluctuations: The strength or weakness of major currencies, particularly the Brazilian real and Indian rupee, can influence sugar export competitiveness and market prices.
-
Demand Fluctuations: Consumer preferences and health trends can also impact sugar demand. There is an increasing global push towards reducing sugar consumption, which could potentially dampen demand over time.
Insights and Future Outlook
The future of the global sugar market will likely be shaped by the resolution of current geopolitical tensions and the stabilization of international trade policies. As countries navigate these uncertainties, market participants should remain vigilant about changes in production forecasts and policy shifts.
In the short term, analysts predict that sugar prices will continue to exhibit volatility, driven by the aforementioned factors. However, the long-term outlook remains cautiously optimistic as advancements in agricultural technology and more predictable trade policies could lead to greater market stability.
Investors and stakeholders should consider these dynamics when making decisions. Diversification and careful monitoring of market indicators, such as weather forecasts and energy prices, will be essential in navigating the sugar market landscape.
Conclusion
The global sugar market is a dynamic arena influenced by a myriad of factors, from weather conditions to trade policies. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about production forecasts and price movements will be crucial for making informed investment decisions. Understanding these trends and their implications can provide valuable insights into future market directions.
By keeping abreast of developments through reliable sources such as Trading Economics, investors can better position themselves to capitalize on opportunities within the sugar market.