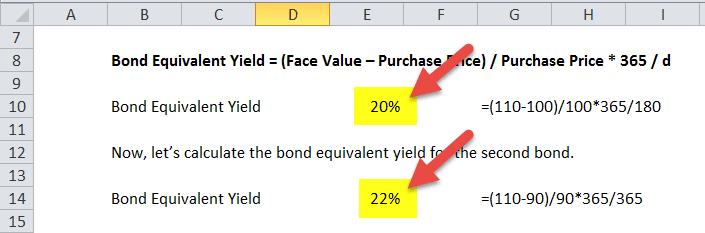
In the intricate world of bond investments, a fundamental understanding of market value and par value is indispensable for astute investors. These concepts are pivotal for determining the yield and potential returns from fixed income securities. Despite their simplicity, the implications of these values can be profound, particularly in volatile interest rate environments.
Market Value vs. Par Value: The Essentials
Market value refers to the current price at which a bond is trading on the open market. It is a dynamic figure, influenced by various factors such as changes in interest rates, economic conditions, and market demand. Conversely, par value is the bond’s face value, or the amount that will be returned to the bondholder at maturity. Typically set at $1,000 for most bonds, par value serves as the benchmark for interest payments, known as the bond's coupon.
To illustrate, consider a bond with a par value of $1,000 and a fixed coupon rate of 5%. Regardless of the bond’s market price, the annual interest payment remains $50. If interest rates rise, the bond’s market value may fall below its par value, making it a discounted bond. Conversely, if interest rates fall, the bond's market price may rise above its par value, categorizing it as a premium bond.
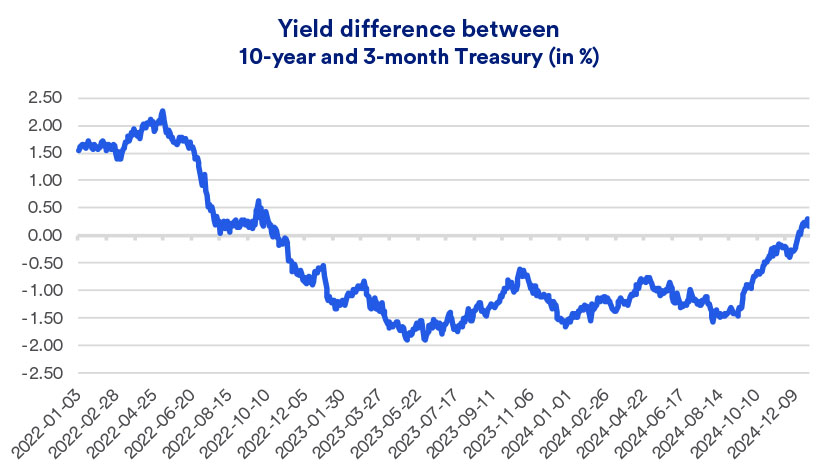
Interest Rate Sensitivity and Market Dynamics
The interplay between interest rates and bond prices, known as interest rate risk, is central to understanding market and par value dynamics. As the Federal Reserve adjusts interest rates, bond prices inversely react. This relationship is encapsulated in the yield curve, which reflects investor sentiment and economic forecasts.
For instance, if the Federal Reserve raises interest rates to curb inflation, existing bonds with lower interest rates become less attractive, and their market value declines. Conversely, when rates are cut to stimulate economic growth, existing bonds with higher rates become more desirable, increasing their market value.
Investment Strategies and Yield Calculations
Investors must consider the market and par value distinction when evaluating bond investments. Yield calculations, which indicate the earnings generated by the bond relative to its market price, are crucial. The current yield is calculated by dividing the annual coupon payment by the bond’s current market price, offering a snapshot of income potential.
Moreover, savvy investors might employ strategies like bond laddering or duration targeting to mitigate interest rate risk and optimize returns. Bond laddering involves purchasing bonds with varying maturities to capture differing interest rates and reduce reinvestment risk. Duration targeting focuses on aligning the bond portfolio’s weighted average duration with interest rate expectations to manage sensitivity to rate changes.
Expert Insights and Market Outlook
According to Kathy Jones, Chief Fixed Income Strategist at Schwab, "Understanding the nuances of market value and par value can significantly influence an investor's ability to navigate the bond market effectively. In today's economic climate, with interest rate volatility, these concepts are more crucial than ever for portfolio management".
Further insights from the Nuveen Fixed Income Commentary reveal that investment-grade corporate and municipal bonds have underperformed Treasuries recently, highlighting the importance of market value fluctuations. The commentary suggests that investors should remain vigilant about economic indicators that could precipitate shifts in bond pricing.
Conclusion: Optimizing Fixed Income Portfolios
Understanding the distinctions between market value and par value is not merely academic; it is a practical skill that can significantly impact investment decisions. By mastering these concepts, investors can better assess the yield and risk profiles of bonds, thereby enhancing their fixed income portfolios' performance.
As the bond market continues to navigate through economic shifts, mastering these fundamentals empowers investors to make informed decisions, optimizing their strategies in an ever-evolving landscape. For further reading and resources, consider exploring Investopedia's primer on par vs. market value.
