
Understanding Cryptocurrency Taxation: Key Insights for Investors
As cryptocurrency trading continues to evolve, the complexities surrounding tax implications become increasingly significant for investors. With the IRS firmly establishing its authority over crypto-related transactions, understanding the tax landscape is crucial to ensuring compliance and optimizing returns. This article delves into the rules governing cryptocurrency taxation, including capital gains and income taxes, to help investors navigate this intricate terrain.

Taxable Events
The IRS categorizes certain cryptocurrency transactions as taxable events. It is essential for investors to recognize these triggers to avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
- Buying and Holding: Merely purchasing cryptocurrency with cash and holding it in a digital wallet does not constitute a taxable event. Taxation arises only when the asset is sold or otherwise disposed of.
- Selling for Cash: When an investor sells cryptocurrency for cash, this transaction incurs capital gains tax if the selling price exceeds the purchase price.
- Receiving Cryptocurrency as Income: Compensation received in cryptocurrency, whether from employment or freelance work, is subject to ordinary income tax.
- Mining Cryptocurrency: Profits gained from mining activities are also taxable and must be reported as income at the fair market value on the day they are received.
Capital Gains Tax
Investors must contend with capital gains tax, which varies based on the duration of asset ownership:
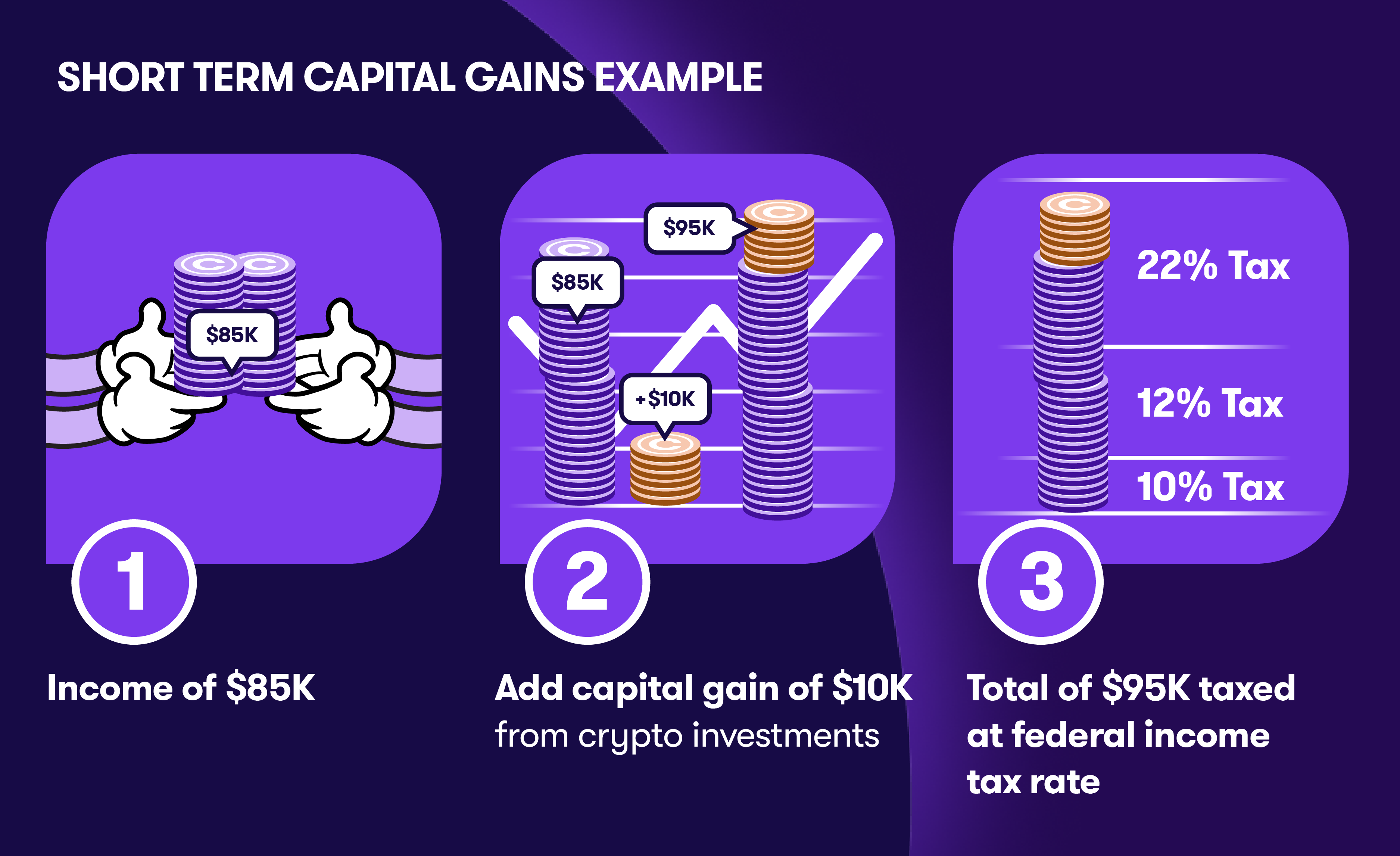
- Short-Term Capital Gains: For assets held for one year or less, gains are taxed as ordinary income, subject to the investor's tax bracket.
- Long-Term Capital Gains: Assets held for longer than one year benefit from a reduced tax rate, incentivizing long-term investment strategies.
According to the IRS, even if the cryptocurrencies are not converted to fiat currency, selling them for a profit still triggers capital gains tax obligations. As noted in a report by NewsNation, “The tax rate depends on how long you hold it before selling.”
Ordinary Income Tax
When investors receive cryptocurrency as payment, it is treated as ordinary income. The taxable amount corresponds to the fair market value of the cryptocurrency at the time of receipt. This includes income earned through mining, which the IRS mandates be reported at its market value on the day it was received.
Losses and Deductions
Just as gains are taxable, losses can mitigate tax liabilities. If an investor sells cryptocurrency for less than its purchase price, this loss can be deducted from taxable income. Investors can deduct up to $3,000 in losses against other income. Should the losses exceed this amount, the remainder can be carried over to subsequent tax years.
Reporting Requirements
The IRS requires investors to report any cryptocurrency income, regardless of whether it is converted to dollars. This includes non-cash transactions, such as gifting cryptocurrency—up to a certain limit—which is also non-taxable. Failing to report these transactions may result in penalties and interest on unpaid taxes.
It’s crucial for investors to maintain accurate records of all transactions, including dates, amounts, and the purpose of each transaction. A comprehensive approach to record-keeping aids in making informed decisions about future transactions and can facilitate easier compliance during tax season.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation is essential for investors aiming to optimize their returns while remaining compliant with IRS regulations. Understanding when transactions trigger taxes and how to effectively report them can significantly impact overall tax liability. As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, the emphasis on transparency and regulatory compliance will only increase, making it imperative for investors to stay informed.
For a detailed understanding of cryptocurrency taxation and how it may affect your financial planning, consult with a tax professional specializing in digital assets. Keeping abreast of IRS guidelines can help protect against unforeseen liabilities and enhance your investment strategy in the dynamic realm of cryptocurrencies.
References

Investors are encouraged to familiarize themselves with these regulations to take full advantage of the growth potential that cryptocurrencies offer while ensuring compliance with tax obligations.