
Understanding Cryptocurrency Taxation: Key Insights for Investors
As the realm of cryptocurrency trading continues to develop and mature, it has become increasingly essential for investors to comprehend the tax implications associated with their transactions. Unlike traditional investments, cryptocurrency transactions can trigger a variety of taxable events recognized by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This article delves into the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation, covering key events such as capital gains and ordinary income taxes, and offers actionable insights for effective tax management.
Overview of Cryptocurrency Taxation
Navigating the world of cryptocurrency can feel akin to traversing the Wild West—exciting yet fraught with uncertainties. With the IRS classifying cryptocurrencies as property rather than currency, a convoluted landscape of taxable events emerges. Investors must be well-versed in these regulations to mitigate tax liabilities effectively.
Taxable Events
-
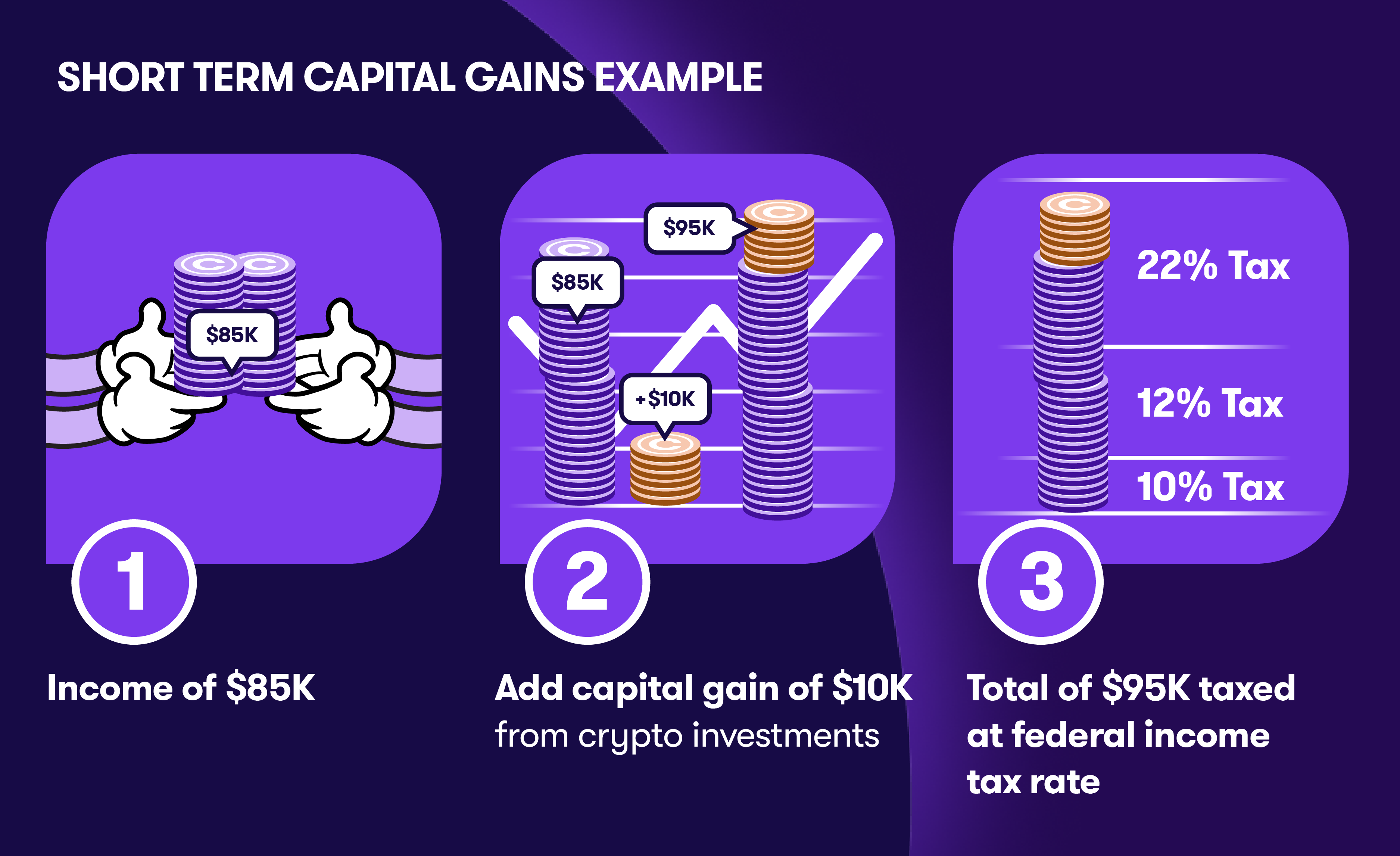
Capital Gains Tax Selling cryptocurrency for cash or trading it for another asset can invoke capital gains tax. This tax applies even if the cryptocurrency is not converted to U.S. dollars. The rate depends on how long the asset was held before the sale:
- Short-term Capital Gains: If an investor owns cryptocurrency for one year or less, they are subject to short-term capital gains tax, which is taxed at their ordinary income tax rate.
- Long-term Capital Gains: If the cryptocurrency is held for more than a year, investors benefit from a lower long-term capital gains tax rate.
According to the IRS, it is crucial for investors to maintain accurate records of their transaction history, including the dates of acquisition and sale, as these will greatly influence the tax owed.
-
Ordinary Income Tax Receiving cryptocurrency as payment for services rendered or through mining is classified as ordinary income. This income is taxed based on the taxpayer's income tax bracket; higher earners pay a steeper rate. For instance, if an individual mines Bitcoin and receives it at a market value of $50,000, that amount is taxable as ordinary income in the year it was received.
Key Considerations
-
Gifts and Transfers: Giving or receiving cryptocurrency as a gift (up to a certain limit) does not trigger a taxable event. Moreover, transferring crypto between wallets owned by the same individual is also free from taxes.
-
Losses: If an investor sells their cryptocurrency for less than the acquisition cost, they can deduct that loss on their taxes, up to $3,000 in most cases. Losses exceeding this limit can be carried forward to offset future gains.
Reporting Requirements
Taxpayers must report all taxable events on their annual tax returns. This includes sales, trades, and income received in cryptocurrency. The IRS has issued a reminder that failure to report cryptocurrency income can lead to penalties and increased scrutiny.
Common Misconceptions
A prevalent misunderstanding among new cryptocurrency investors is that buying cryptocurrency and simply holding it does not incur taxes. While holding assets does not trigger tax liabilities, selling or trading them does. Additionally, unrealized gains (increases in value without selling) are not subject to taxation until realized through a sale.

Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of cryptocurrency taxation is paramount for investors aiming to optimize their tax liabilities and ensure compliance with IRS regulations. Keeping accurate records and being aware of different taxable events can help mitigate potential tax burdens, enhancing overall investment strategies.
As cryptocurrency continues to proliferate, investors should remain informed about both the tax implications and the evolving regulatory landscape. The IRS has shown a commitment to enforcing compliance in this area, making it increasingly vital for cryptocurrency participants to stay up-to-date on tax obligations.
For further guidance, investors may consult tax professionals with expertise in cryptocurrency transactions or explore resources provided by the IRS, such as Publication 547, which outlines the tax treatment of capital gains and losses.

In a world where digital assets are becoming increasingly mainstream, understanding cryptocurrency taxation isn't just beneficial—it's essential for responsible investing and financial planning.