Analyzing the Shift Towards Catastrophe Bonds in Fixed Income Investment

In recent years, catastrophe bonds have emerged as a vital component of the fixed income landscape, particularly in the context of increasing natural disasters and climate-related risks. With their unique structure, these bonds offer investors a way to gain exposure to the insurance market while providing issuers with crucial capital for disaster recovery.
The Growth of Catastrophe Bonds
As of March 2025, catastrophe bonds comprise 32% of the California Earthquake Authority's reinsurance tower, showcasing their growing importance in managing risks associated with natural disasters. This trend reflects a broader shift in the investment community towards instruments that can provide both yield and a hedge against catastrophic events. The increasing prevalence of climate-related incidents has triggered a demand for innovative financial solutions that can address both risk management and investment objectives.
Market Dynamics
The issuance of catastrophe bonds has surged, driven by heightened awareness of climate risks and the need for creative financial solutions. According to Environmental Finance, the sustainable bond market has now surpassed $6 trillion in cumulative issuance, indicating a strong appetite for environmentally-focused investment strategies. Investors are increasingly attracted to these bonds due to their potential for higher yields compared to traditional fixed income securities, coupled with the diversification benefits they offer.
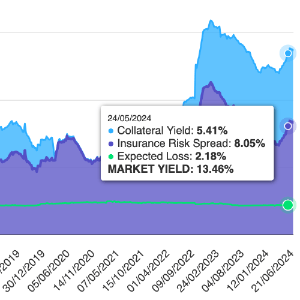
For instance, the average yield on catastrophe bonds currently stands at around 6%, while conventional bonds often yield lower returns. This yield differential is particularly appealing in an environment where fixed income investors are grappling with low interest rates and rising inflationary pressures.
Risk and Return Considerations
While catastrophe bonds can yield attractive returns, they also come with inherent risks, including the potential for total loss if a specified disaster occurs. Investors must weigh these risks against their overall portfolio strategy and risk tolerance. The unique nature of catastrophe bonds means that they can be seen as a high-risk, high-reward investment vehicle.
For example, data shows that in previous years, certain catastrophe bonds faced payouts due to unforeseen natural disasters, resulting in significant losses for some investors. However, the potential for substantial returns continues to draw interest, particularly as institutions seek to enhance their fixed income allocations with diversified strategies.
Investor Interest and Implications
The growing interest in catastrophe bonds has implications for institutional investors, including pension funds and insurance companies, who are increasingly recognizing the value of incorporating these financial instruments into their investment portfolios. The increasing integration of catastrophe bonds into risk management frameworks reflects a segmentation of risk that allows investors to better navigate the uncertainties posed by climate change.
According to a report by Artimis, the market has been expanding rapidly, with issuance hitting record levels in recent years. This is indicative of a broader trend where climate-related financial instruments are becoming essential in mitigating potential risks associated with environmental factors.

Conclusion
As the fixed income market continues to evolve, catastrophe bonds represent a compelling opportunity for investors looking to diversify their portfolios while addressing the growing challenges posed by climate change. The dual role of these financial instruments—as both a response to environmental risks and a potential source of attractive yields—highlights their increasing significance in the modern investment landscape.
Understanding the dynamics of catastrophe bonds, including their potential returns and associated risks, will be essential for making informed investment decisions in the coming years. As more investors seek stability amidst economic uncertainty, catastrophe bonds may well become a cornerstone of diversified fixed income strategies.
References
For further information on the catastrophe bond market and its implications for investors, visit Environmental Finance.