
The Strategic Shift Towards Catastrophe Bonds in Fixed Income Investments
In recent months, the fixed income landscape has witnessed a notable shift towards catastrophe bonds, driven by escalating climate-related risks and the need for innovative financial solutions. As extreme weather events become more common and impactful, these bonds offer investors competitive yields while addressing pressing environmental concerns. Institutions and individual investors alike are beginning to recognize the potential of catastrophe bonds as a viable component of their portfolios.
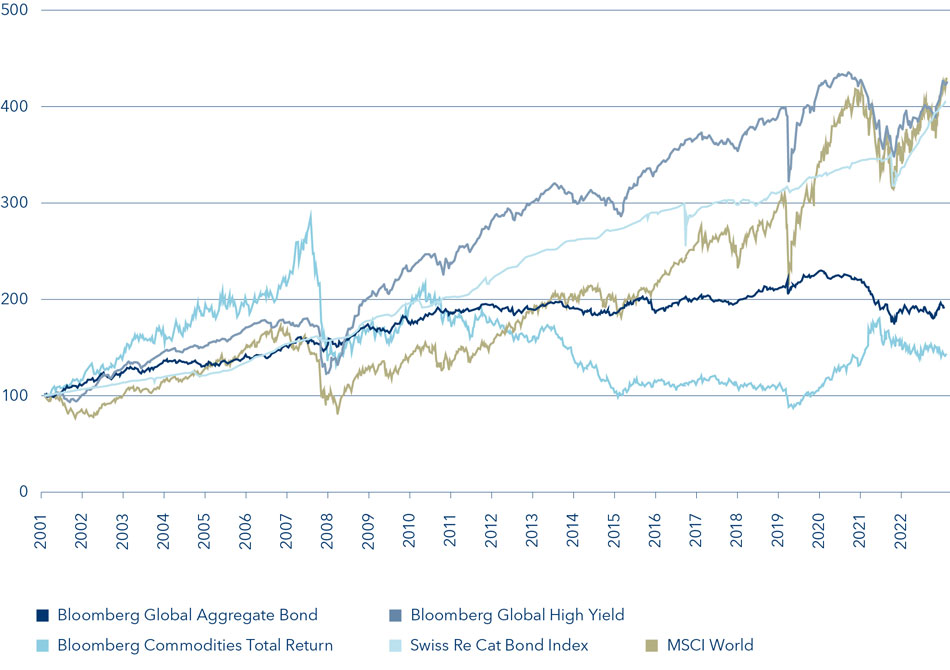
Market Dynamics
Catastrophe bonds, or cat bonds, are designed to transfer the risk of natural disasters from insurers to investors. Essentially, they serve as a form of insurance for insurance companies, providing a unique investment opportunity that aligns with the growing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. According to the California Earthquake Authority, as of March 2025, catastrophe bonds have been integrated into 32% of its reinsurance strategy, underscoring their critical role in managing natural disaster risks.
The increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters—hurricanes, floods, wildfires—have made the traditional insurance model less viable, prompting insurers to seek alternative solutions. Cat bonds not only help insurers manage their risk exposure but also offer investors a chance to earn attractive returns while contributing to societal resilience against climate change.
Yield and Performance
Currently, catastrophe bonds are yielding approximately 6%, making them an appealing option for investors seeking higher returns in a low-interest-rate environment. This yield is competitive when compared to traditional fixed income instruments, which often struggle to offer appealing returns, especially in a climate where central banks around the world have kept interest rates low or even negative.
Investors are becoming increasingly aware of the potential for climate-related events to impact their portfolios, leading to a strategic shift towards instruments that not only hedge against these risks but also deliver attractive yields. The market for catastrophe bonds has been expanding, with total issuance reaching $10 billion in 2024, according to industry sources.

The Role of Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, including pension funds and insurance companies, are increasingly allocating funds to catastrophe bonds. This trend is driven by a combination of factors, including the desire for portfolio diversification and the recognition that climate risks are systemic and can have far-reaching implications.
A report from Artemis, a leading source of data regarding insurance-linked securities, noted that catastrophe bonds are likely to play an even larger role in institutional portfolios as the understanding of climate risk deepens. "The integration of cat bonds into portfolios not only enhances yield but serves as a strategic response to the evolving landscape shaped by climate change,” said a representative from Artemis.
Furthermore, as institutional investors face increasing pressure to adhere to ESG principles, catastrophe bonds fit seamlessly into the broader narrative of sustainable investing, appealing to those looking to align their investment strategies with their values.
The Future Outlook
The future of catastrophe bonds looks promising, particularly as awareness of climate-related financial risks grows. Financial regulators around the globe are beginning to recognize the need for robust frameworks to manage these risks, potentially leading to increased demand for cat bonds. The market could expand even further as more countries adopt similar models to the California Earthquake Authority, which has set a precedent for integrating catastrophe bonds into public policy.
Moreover, the launch of new products aimed at retail investors could democratize access to these investment vehicles, allowing a broader range of investors to participate in the cat bond market. As these products evolve, they may appeal to a growing demographic of environmentally-conscious investors seeking to make impactful investment choices.
Conclusion
The increasing adoption of catastrophe bonds reflects a strategic shift in fixed income investments, as investors seek to balance risk management with the pursuit of sustainable returns. As the market for these bonds continues to expand, they present a compelling opportunity for those looking to enhance their fixed income allocations while addressing pressing environmental challenges.
Investors are encouraged to consider the benefits of catastrophe bonds not only for their potential yields but also for their role in fostering resilience against the growing threat of climate change. With the right approach, catastrophe bonds could become a cornerstone of a modern, sustainable investment strategy.
For more insights on the catastrophe bond market, investors can refer to resources such as Artemis, which provides comprehensive data and analysis on insurance-linked securities. As the landscape evolves, staying informed will be essential for making sound investment decisions in this dynamic arena.