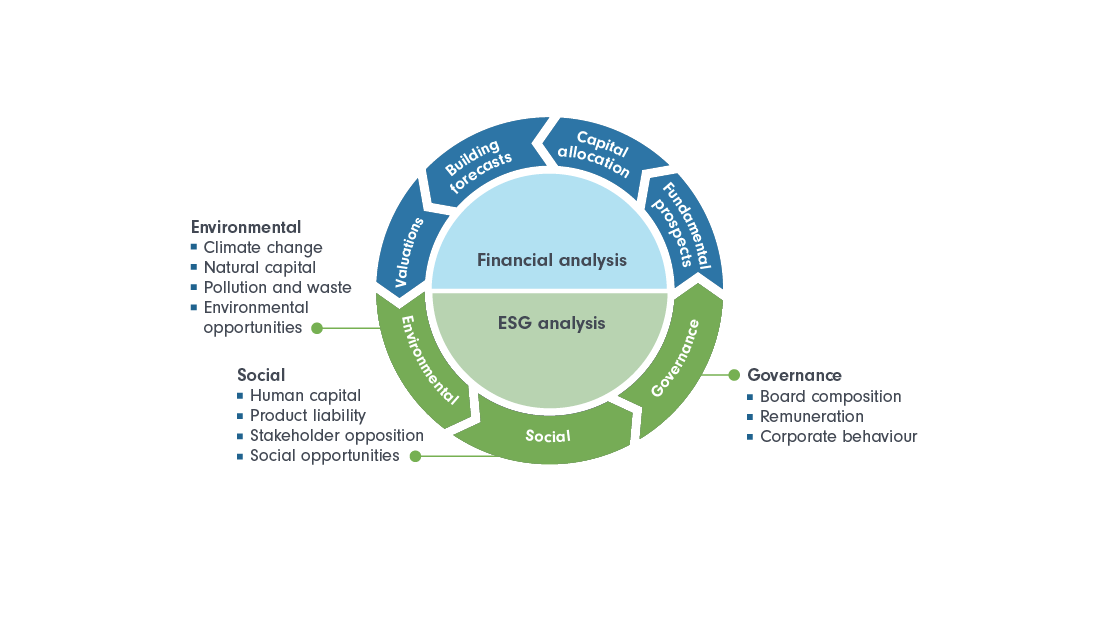
The Rise of Sustainable ETFs: Navigating the Growing Market
In recent years, the investment landscape has undergone a remarkable transformation, with a notable shift towards sustainable investing. As more investors prioritize their values alongside financial goals, Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) that focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria have emerged as key players in this evolving market. This article delves into the current trends in sustainable ETFs, assesses their performance compared to conventional funds, and explores the implications for investors navigating this burgeoning sector.
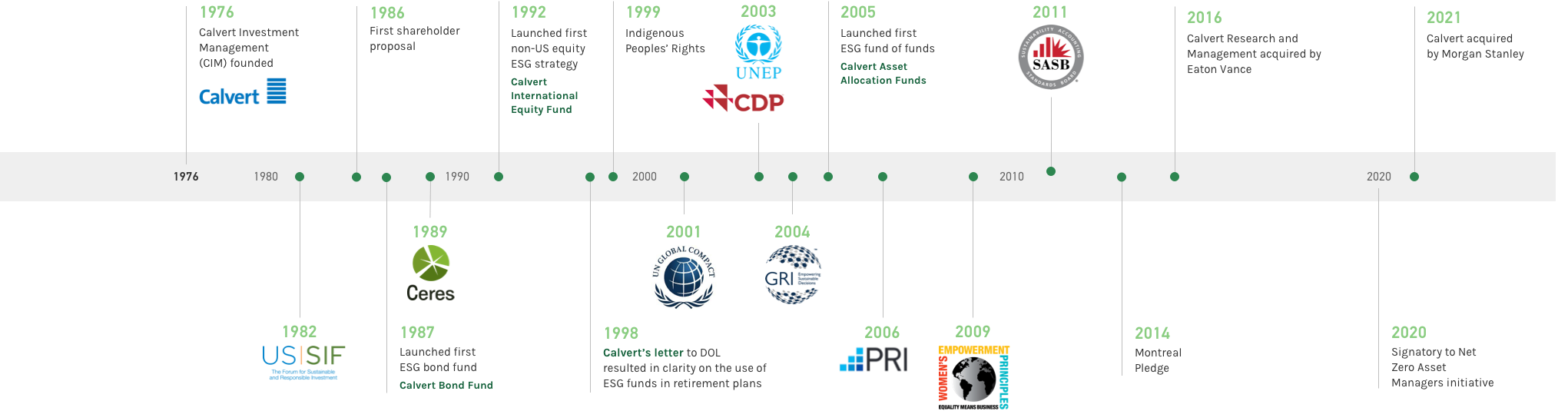
Current Market Trends
As of 2024, sustainable ETFs have significantly gained traction, accounting for approximately 20% of total sustainable fund assets. This growth trajectory is underscored by net inflows of $43.5 billion into sustainable ETFs, with Europe leading the charge at $29.6 billion. Such figures highlight an increasing investor preference for funds that not only align with their ethical beliefs but also seek to deliver competitive returns.
According to a report from ISS Governance Insights, the majority of sustainable assets under management (AUM) are concentrated in Europe and North America, with these regions representing nearly 97% of the sustainable fund assets globally. The data suggests that as societal awareness of ESG issues continues to rise, investors are increasingly gravitating towards funds that prioritize sustainability.
Performance Analysis
Despite facing a challenging economic environment, sustainable ETFs have demonstrated resilience. The growth rate of sustainable ETF assets has consistently outpaced that of conventional ETFs, signaling a shift in investor sentiment towards sustainable investment strategies. The global sustainable ETF market is currently valued at $555 billion, significantly larger than the approximately $15 trillion overall ETF market.
A comparative analysis reveals that sustainable ETFs have not only performed well during market downturns but have also shown competitive returns over longer periods. Investors looking for both ethical alignment and strong financial performance are finding these funds an attractive option. For example, while conventional funds have experienced varying levels of volatility, sustainable ETFs have managed to retain investor confidence, as highlighted by their robust inflow figures.
Implications for Investors
Investing in sustainable ETFs presents an opportunity for investors to diversify their portfolios while adhering to ESG principles. These funds provide exposure to companies with strong sustainability practices and robust governance structures, which can lead to long-term financial stability. Furthermore, as investor demand for sustainable investment options continues to grow, it is likely that the performance metrics of these funds will further improve.
A survey by Morningstar revealed that nearly half of institutional investors are now considering increasing their allocations to sustainable investments, reflecting a broader trend toward sustainability in capital markets. This shift not only emphasizes the ethical implications of investing but also highlights the potential for sustainable ETFs to deliver strong financial returns.
Conclusion
The demand for sustainable investment options is at an all-time high, with ESG-focused ETFs becoming essential components of modern investment strategies. As the market for sustainable ETFs continues to evolve, investors should consider these funds not only for their ethical implications but also for their potential to yield robust financial returns over the long term.
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, the rise of sustainable ETFs is a testament to the changing dynamics of investment strategy. For investors, aligning financial goals with personal values through sustainable investing could be a pathway to achieving both social impact and economic benefit.
References

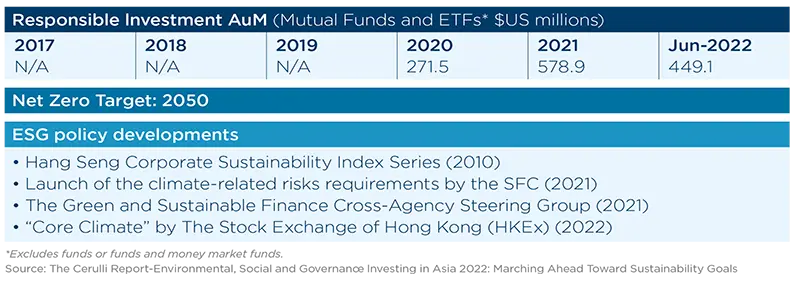
As we navigate this evolving market, the growth of sustainable ETFs represents not just a trend but a fundamental shift in how investors perceive their roles in shaping a sustainable future.