Emerging Trends in ESG Integration within Global Equity ETFs: Implications for Portfolio Construction in 2025

Source: State Street Global Advisors
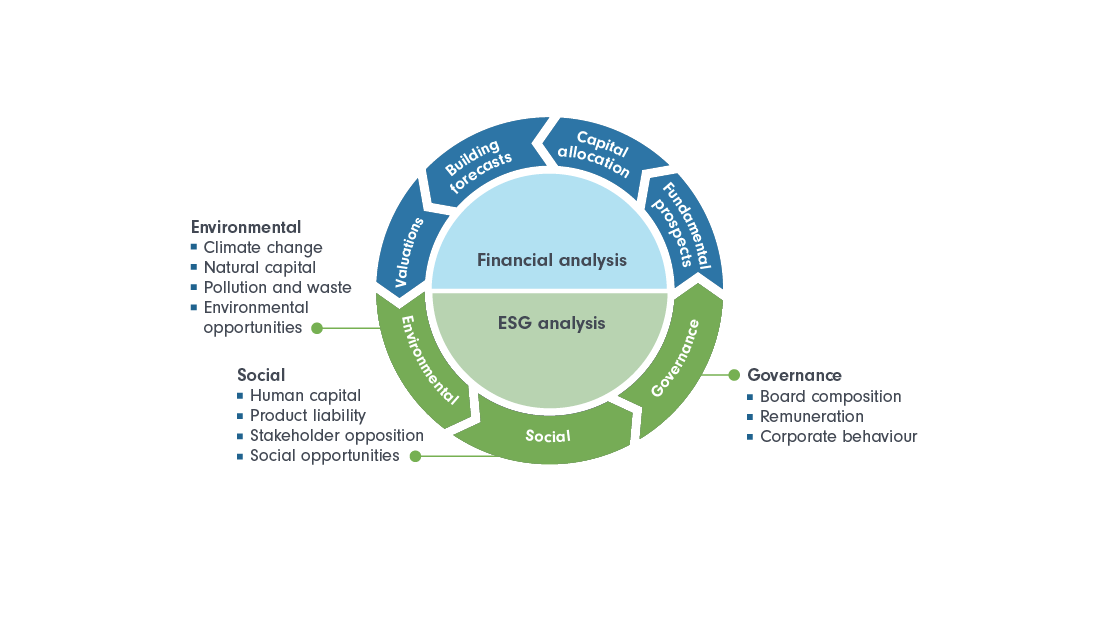
In 2025, Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) integration within global equity Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) has rapidly evolved from a specialized niche into a mainstream pillar of portfolio construction worldwide. This transition is driven by a confluence of regulatory pressures, investor demand for sustainable investing solutions, and enhanced data transparency. As ESG-focused ETFs reshape investment landscapes, institutional and retail investors are re-examining portfolio strategies to balance financial returns with sustainability imperatives more effectively.
Market Dynamics Driving ESG ETF Growth
The global surge in ESG ETF assets under management (AUM) is notable. According to data synthesized from major asset managers such as State Street and BlackRock’s iShares platform, inflows into ESG-related equity ETFs have accelerated sharply in 2025, propelled by:
-
Regulatory Frameworks: The European Union’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) has set a high bar for transparency and sustainability disclosures, influencing fund structures. Similar frameworks in the United States, including the SEC’s enhanced ESG disclosure rules, and emerging regulatory initiatives in Asia-Pacific markets have collectively mandated greater ESG integration in investment products.
-
Corporate Net-Zero Commitments: Many large-cap companies indexed within global equity ETFs have adopted net-zero carbon emission targets, which in turn shift index compositions to favor companies with credible decarbonization strategies. This corporate pivot is reflected in the sectoral weightings within ESG ETFs.
-
Advancements in ESG Data and Scoring: The proliferation of sophisticated ESG data providers and third-party rating agencies has improved the granularity and comparability of ESG scores. Enhanced transparency enables ETF issuers to refine screening methodologies and tailor portfolios towards sustainability leaders.
The combined effect of these drivers is a sustained expansion of ESG ETF offerings, ranging from broad global ESG indices to thematic funds targeting clean energy, diversity-focused companies, and sustainable innovation.
Performance Differentials and Risk Management Enhancements
Contrary to early skepticism about potential performance trade-offs, ESG ETFs in 2025 have demonstrated competitive, and in some cases superior, risk-adjusted returns relative to traditional equity benchmarks. This is particularly evident in sectors such as clean energy and technology, which have outperformed due to favorable regulatory tailwinds and innovation-driven growth.
Data from iShares and State Street indicate that ESG-integrated portfolios have shown:
-
Improved Downside Protection: During recent market volatility episodes, ESG ETFs experienced less severe drawdowns compared to conventional equity ETFs. Stronger governance frameworks and robust environmental stewardship contribute to company resilience, enhancing portfolio stability.
-
Sectoral Rotation: Traditional fossil fuel sectors have faced headwinds driven by transition risks and investor divestment trends, while renewable energy, sustainable infrastructure, and responsible consumer goods sectors have gained increased allocations.
-
Volatility Profiles: ESG funds tend to exhibit slightly lower beta and volatility, which supports a more stable return profile over both short and medium-term horizons.
This evolving performance landscape positions ESG ETFs as not only value-aligned vehicles but also as strategic tools for risk mitigation.
Portfolio Construction Implications for Investors
The widespread adoption of ESG ETFs offers investors a versatile framework to embed sustainability without sacrificing diversification or financial objectives. Key implications include:
-
Diversification Benefits: ESG ETFs provide exposure to a universe of companies demonstrating leadership in sustainability practices, often spanning multiple regions and sectors. This exposure enhances portfolio diversification by incorporating non-traditional factors linked to long-term environmental and social trends.
-
Alignment with Fiduciary Duties: Institutional investors face increasing mandates to consider ESG factors as part of fiduciary responsibility, emphasizing stewardship and long-term value creation. ESG ETFs fulfill these obligations while maintaining liquidity and cost efficiency.
-
Mitigation of Regulatory and Reputational Risks: By tilting portfolios toward companies with robust ESG practices, investors reduce exposure to regulatory penalties, litigation, and reputational damage that can arise from environmental or social controversies.
-
Thematic and Strategic Allocation: Investors are increasingly layering ESG thematic ETFs such as those focused on global clean energy or gender diversity alongside core ESG equity funds, enabling more granular tactical asset allocation.
Large asset managers continue to enhance ESG ETF product suites, allowing customization for various risk-return profiles and sustainability objectives.
Challenges and Considerations in ESG ETF Adoption
Despite the robust growth and integration, challenges remain that require investor vigilance:
-
Heterogeneity in ESG Ratings and Methodologies: ESG rating agencies often differ significantly in their assessments due to varying criteria and weighting schemes. This variability can lead to inconsistent portfolio exposures and complicate benchmarking.
-
Trade-Offs Between ESG and Traditional Financial Metrics: Some companies with strong ESG scores may exhibit lower financial metrics or higher valuations, creating potential conflicts in portfolio construction.
-
Dynamic Nature of ESG Disclosures: Continuous changes in corporate ESG disclosures and emerging controversies necessitate active monitoring to manage reputational and compliance risks effectively.
-
Greenwashing Risks: The growing market attracts scrutiny over ESG claims, emphasizing the need for due diligence and transparent reporting standards.
Investors are advised to integrate ESG data analysis with traditional financial analysis and maintain an adaptive governance approach to ESG investing.
Conclusion
The integration of ESG criteria within global equity ETFs in 2025 marks a transformative phase in investment management. ESG ETFs are no longer peripheral but central to constructing portfolios that meet evolving regulatory standards, investor expectations, and sustainability goals. For investors—from institutional asset allocators to retail participants—understanding the nuances of ESG ETF construction, performance implications, and risk management is critical in harnessing their full potential.
As the ESG landscape continues to mature, investors who strategically incorporate ESG ETFs into their portfolios will be better positioned to achieve resilient financial performance while advancing sustainability imperatives.
References

Robust ESG integration enhances portfolio risk management — CentralEyes
Author: [Your Name]
Date: July 13, 2025