
Emerging Trends and Strategic Outlook for Palm Oil Markets in Mid-2025
As the global economy navigates complex sustainability imperatives and shifting demand patterns, the palm oil market in mid-2025 reflects a nuanced balance of stability and evolving challenges. Traded extensively through contracts for difference (CFDs) tracking benchmark prices, palm oil continues to be a linchpin commodity widely used in food products, biofuels, and industrial applications. This analysis delves into critical supply-side dynamics, regulatory pressures, logistics complexities, and demand trends shaping the palm oil landscape today, offering investors and market participants actionable insights amidst ongoing market transformation.
 Source: Nuffood Spectrum Asia
Source: Nuffood Spectrum Asia
Supply and Production Foundations: Indonesia and Malaysia’s Dominance
Indonesia and Malaysia remain the pillars of global palm oil production, jointly accounting for approximately 85% of worldwide supply. Production volumes this year have demonstrated relative steadiness following prior fluctuations, yet the sector grapples with persistent operational challenges that could disrupt supply continuity.
-
Weather Variability: Climatic anomalies, including irregular rainfall and localized droughts, have introduced uncertainties affecting palm fruit yields and harvesting schedules.
-
Labor Shortages: Increasing labor costs and migration shifts have tightened available workforce pools on plantations, pressuring processing throughput and elevating operational expenses.
-
Logistical Bottlenecks: Freight constraints, port congestion, and container shortages have exacerbated transportation delays, impacting delivery timelines and inflating costs.
These factors collectively create a fragile equilibrium where supply steadiness masks underlying vulnerabilities, requiring close monitoring by traders and supply chain managers.
Sustainability Pressures: Regulatory and Consumer-Driven Imperatives
Sustainability considerations have ascended to the forefront of palm oil market dynamics, propelled by a convergence of regulatory frameworks and heightened consumer awareness. Certified Sustainable Palm Oil (CSPO) has transitioned from a niche segment to a baseline expectation for market access, especially in stringent regions such as the European Union.
-
Regulatory Environment: The EU’s tightening regulations concerning bio-based products, environmental impact disclosures, and import sustainability compliance are reshaping sourcing strategies. Palm oil producers aiming to maintain or enhance market channels must align with standards such as the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) and the International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC).
-
Traceability and Certification: Transparency across the supply chain is gaining importance, with blockchain and digital traceability solutions emerging as critical tools to validate certifications and uphold environmental commitments.
-
Consumer Expectations: End-market buyers increasingly demand assurances of deforestation-free practices, fair labor standards, and reduced carbon footprints, impacting procurement policies of multinationals and retailers.
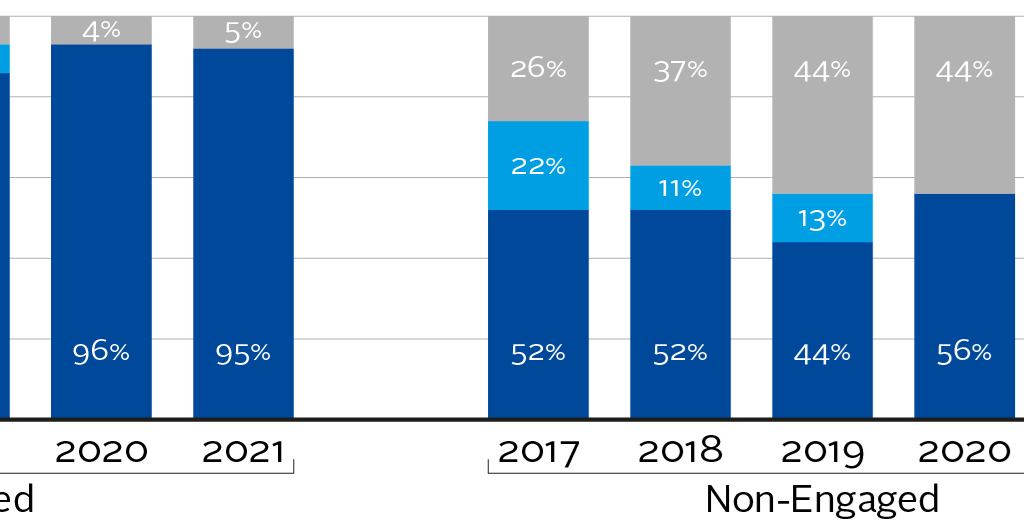 Source: Chain Reaction Research
Source: Chain Reaction Research
These drivers not only influence corporate social responsibility profiles but also bear directly on investment valuations and risk assessments within the palm oil sector.
Trade and Freight: Navigating Volatility in Shipping and Logistics
Global trade flows of palm oil are increasingly complicated by volatile freight rates and shifting geopolitical undercurrents. Market intelligence platforms such as CM Navigator have become indispensable in providing real-time insights into freight costs and commodity pricing, enabling stakeholders to manage emerging risks effectively.
-
Fluctuating Fuel Prices: Volatility in bunker fuel costs directly raises shipping expenses, which are passed through to commodity prices and erode profit margins.
-
Port Congestion: Key export hubs in Indonesia and Malaysia face delays due to labor disputes, infrastructure limitations, and increasing shipment volumes, compounding transit time uncertainties.
-
Geopolitical Tensions: Trade disputes and tariff fluctuations between major economies occasionally disrupt established routes, compelling traders to seek alternative logistics solutions or incur premium costs.
This complex logistics environment necessitates agile supply chain management and proactive hedging to shield against cost overruns and delivery disruptions.
Demand Trends: Growth in Emerging Markets, Shifts in OECD Consumption
Emerging markets, notably India and China, are propelling palm oil demand growth, driven by expanding populations, rising incomes, and increased use in food and industrial sectors. Conversely, consumption patterns in OECD countries reveal signs of moderation or transformation under environmental scrutiny and evolving dietary preferences.
-
India and China: These markets absorb increasing volumes of palm oil, motivated by competitive pricing, versatility, and biofuel mandates.
-
OECD Countries: Heightened environmental concerns, consumer shifts towards alternative oils, and regulatory pressures are contributing to a plateau or decline in traditional palm oil consumption.
Investors should weigh these divergent trends carefully, considering the geographic composition of exposure and evolving regulatory landscapes in destination markets.
Investment Implications: Positioning for Sustainability and Operational Excellence
The palm oil market in 2025 presents nuanced investment opportunities for those emphasizing sustainability credentials and operational adaptability.
-
Sustainability Leadership: Firms with robust CSPO certification, transparent supply chains, and demonstrated environmental stewardship are likely to sustain premium market access and mitigate reputational risks.
-
Technological Adoption: Blockchain-enabled traceability and precision agriculture technologies offer competitive advantages, enhancing efficiency and compliance.
-
Risk Management: Given price volatility and logistics uncertainties, hedging through futures and options remains a critical strategy to protect margins.
-
Supply Chain Agility: Companies that can navigate freight volatility and rapidly adjust sourcing and distribution channels will outperform peers in this dynamic market.
Investors and market participants should integrate these factors into portfolio assessments and strategic planning to harness upside potential while managing systemic risks.
 Source: MDPI Foods
Source: MDPI Foods
Conclusion
As of mid-2025, the palm oil market exemplifies a commodity sector balancing steady production with intricate challenges linked to sustainability, supply chain logistics, and shifting global demand. Indonesia and Malaysia’s production steadfastness provides foundational stability even as environmental regulations and market expectations intensify. Freight and trade complexities necessitate agile risk management, while emerging market growth contrasts with OECD consumption shifts.
For investors and industry stakeholders, success hinges on embracing sustainability imperatives, leveraging technology for supply chain transparency, and executing disciplined hedging in an environment marked by cost pressures and regulatory evolution. Keeping abreast of these trends will be critical to capitalizing on opportunities and mitigating risks in the global palm oil marketplace.
References
- Trading Economics Palm Oil Data: https://tradingeconomics.com/commodity/palm-oil
- CM Navigator Freight and Commodity Market Intelligence: https://cmnavigator.com/
Published July 14, 2025